In an era where data is a precious asset and cyber threats loom large, ensuring the security of data stored in the cloud is of paramount importance. With businesses and individuals increasingly relying on cloud services for storage, applications, and more, adopting robust cloud security practices is no longer optional. This blog will delve into essential cloud security best practices to help safeguard your digital assets.
Understanding Cloud Security
Before diving into best practices, it’s essential to understand the nature of cloud security. Cloud security is a set of policies, technologies, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and the cloud infrastructure itself. It encompasses the shared responsibility model between cloud service providers and customers. While cloud providers ensure the security of their infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing their data and applications.
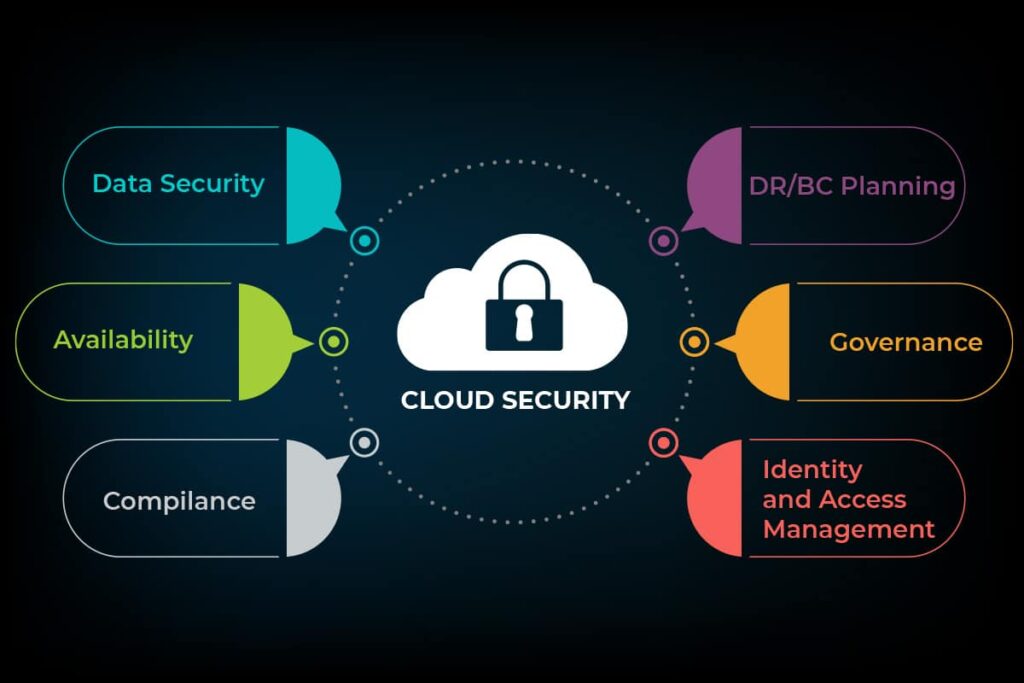
Best Practices For Cloud Security
-
Data Encryption:
Data encryption is the cornerstone of cloud security. Ensure that all sensitive data is encrypted both at rest and in transit. At rest, data encryption involves securing information stored on physical media, such as hard drives or solid-state drives. Cloud providers often offer encryption services and key management systems that make encryption relatively straightforward. Encrypting data in transit, on the other hand, ensures that information is protected while being transmitted over networks. Employ secure communication protocols, such as HTTPS and VPNs, to safeguard data during transmission.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to user access. Additionally, the implementation of multifactor authentication significantly bolsters security measures. In this context, users are required to supply not only their password but also one or more supplementary verification components, which may include a fingerprint scan, facial recognition, or a temporary code dispatched to their mobile device. Consequently, this multifaceted approach to authentication serves to considerably elevate the complexity involved in unauthorized individuals trying to infiltrate cloud accounts. Even in cases where these malicious actors have managed to obtain the user’s password, the additional verification factors act as robust safeguards, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. This robust defense mechanism effectively safeguards sensitive data and bolsters the security of cloud resources. Implementing MFA is a practical way to prevent unauthorized access
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM):
Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies are crucial for maintaining security within the cloud environment. Implement a least-privilege model, meaning that users are granted only the minimum level of access required to fulfill their job roles. Regularly audit and review access permissions to minimize the risk of unauthorized access or accidental data exposure. IAM tools offered by cloud providers enable organizations to control who has access to specific cloud resources, making it easier to enforce the principle of least privilege.
-
Regular Updates and Patch Management:
Cloud security doesn’t end at initial setup. Ongoing maintenance, including regular updates and patch management, is crucial to mitigating security risks. Cloud-based resources, including virtual machines and cloud applications, should be frequently updated with security patches. Many cyberattacks exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. Ensuring that your cloud environment remains up to date reduces the potential attack surface and enhances the overall security posture
-
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Implement comprehensive security monitoring solutions that continuously analyze system activities and network traffic for signs of intrusion or unusual behavior. Advanced security information and event management (SIEM) tools detect suspicious activities and trigger alerts for investigation. It’s essential to have a well-defined incident response plan in addition to monitoring. This plan should outline the actions to take in the event of a security breach or cyberattack, ensuring that your team is prepared to react swiftly and effectively to mitigate damage.
-
Cloud Security Training:
The human element is often the weakest link in security. To address this vulnerability, ensure that your organization’s personnel, from IT staff to end-users, are well-trained in cloud security best practices. Regular training can help staff recognize and mitigate threats effectively. Empower your team with the knowledge to identify potential risks, avoid phishing attacks, and adhere to security policies. By promoting a culture of security awareness, you reduce the risk of human error that could lead to security breaches.
-
Backup and Disaster Recovery:
While focusing on prevention, it’s equally important to prepare for the worst-case scenario. Regularly back up your data and establish a disaster recovery plan. This ensures that even in the event of data loss or a cyberattack, your data remains accessible and intact. Cloud-based backup and recovery solutions make this process more straightforward, offering scalable and cost-effective options to safeguard data and ensure business continuity.
-
Compliance and Regulations
Compliance with industry-specific standards and regulations is crucial for many businesses. Depending on your industry and geographical location, various regulations may apply to your data. Stay informed about these standards and ensure that your cloud security practices align with compliance requirements. Failing to meet compliance standards can result in legal consequences and damage to your organization’s reputation. Many cloud providers offer compliance tools and certifications to assist businesses in meeting these requirements.
-
Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing:
Regularly scan your cloud infrastructure and applications for vulnerabilities. Utilize automated vulnerability scanning tools to identify and prioritize weaknesses. Additionally, perform penetration testing. This process simulates cyberattacks on your cloud infrastructure to assess its security robustness. Such measures assist in identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities. It’s important to resolve these issues before potential threats exploit them, thus minimizing the chances of data breaches or system compromises.

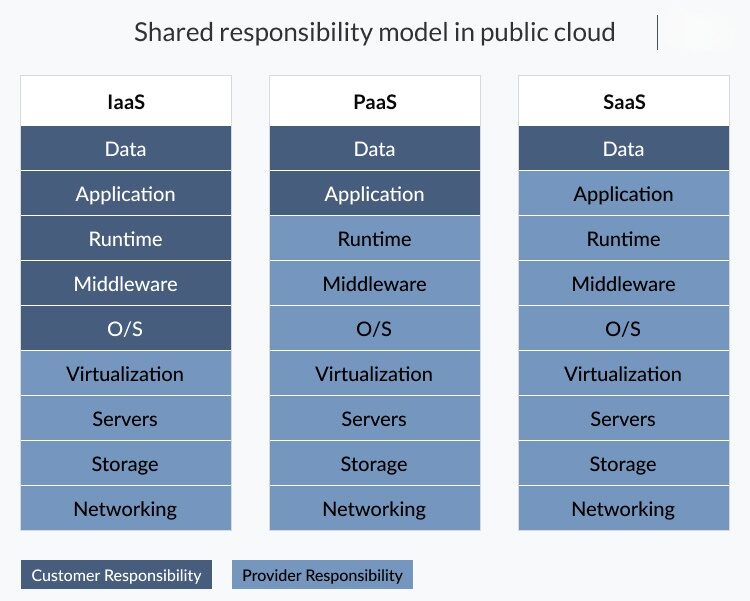
The Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud security necessitates adherence to the shared responsibility model. Major cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, take care of securing their infrastructure. Nonetheless, users bear the essential responsibility for the protection of their data and applications. Within this context, it’s imperative to grasp that, while cloud providers diligently oversee the security of their infrastructure, users play a pivotal role in ensuring the safeguarding of their data and applications stored in the cloud environment. By comprehending this shared responsibility model, individuals and organizations can effectively reinforce their overall security posture in the cloud. Furthermore, it’s critical to recognize that security in the cloud transcends infrastructure-level protection. Users must actively engage in implementing robust data encryption, access control policies, and other security mechanisms. By embracing these fundamental cloud security practices, you can enhance the protection of your digital assets and confidently harness the advantages of cloud technology.
Conclusion
As cloud technology continues to shape our digital world, ensuring cloud security best practices remains a pressing concern. Individuals and businesses can enjoy the cloud’s advantages. They can do this by implementing robust security practices, staying updated with evolving threats, and fostering a culture of security awareness. Data security in the cloud is a shared responsibility. With these best practices, you’re well on your way to safeguarding your digital assets effectively.
Click here To know more about this Cloud & Microservices Based OTT Platforms .


