In the ever-evolving digital landscape, data stands as the lifeblood of modern enterprises. Its generation, collection, storage, and accessibility play pivotal roles in shaping business operations and strategic decisions. Enter the realm of cloud data storage solutions, a transformative force that has revolutionized the way organizations manage, store, and harness their data assets.
Understanding Cloud Data Storage Solutions
Before we embark on our journey into the depths of cloud data storage, it’s essential to grasp the foundation of this paradigm. At its core, cloud data storage represents a fundamental shift from traditional data storage methods, where physical infrastructure, such as servers and data centers, was the norm. With cloud storage, data is hosted, managed, and made accessible through remote cloud servers.
Cloud Storage vs. Cloud Databases:
It’s vital to distinguish between cloud storage and cloud databases. While the terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct yet interconnected elements in the cloud computing landscape. Cloud storage primarily focuses on storing and managing unstructured or semi-structured data, such as files, images, videos, and backups. In contrast, cloud databases are designed for structured data, like customer information or transaction records. Understanding this differentiation is fundamental, as it determines the type of service you require for your data.
Varieties of Cloud Storage:
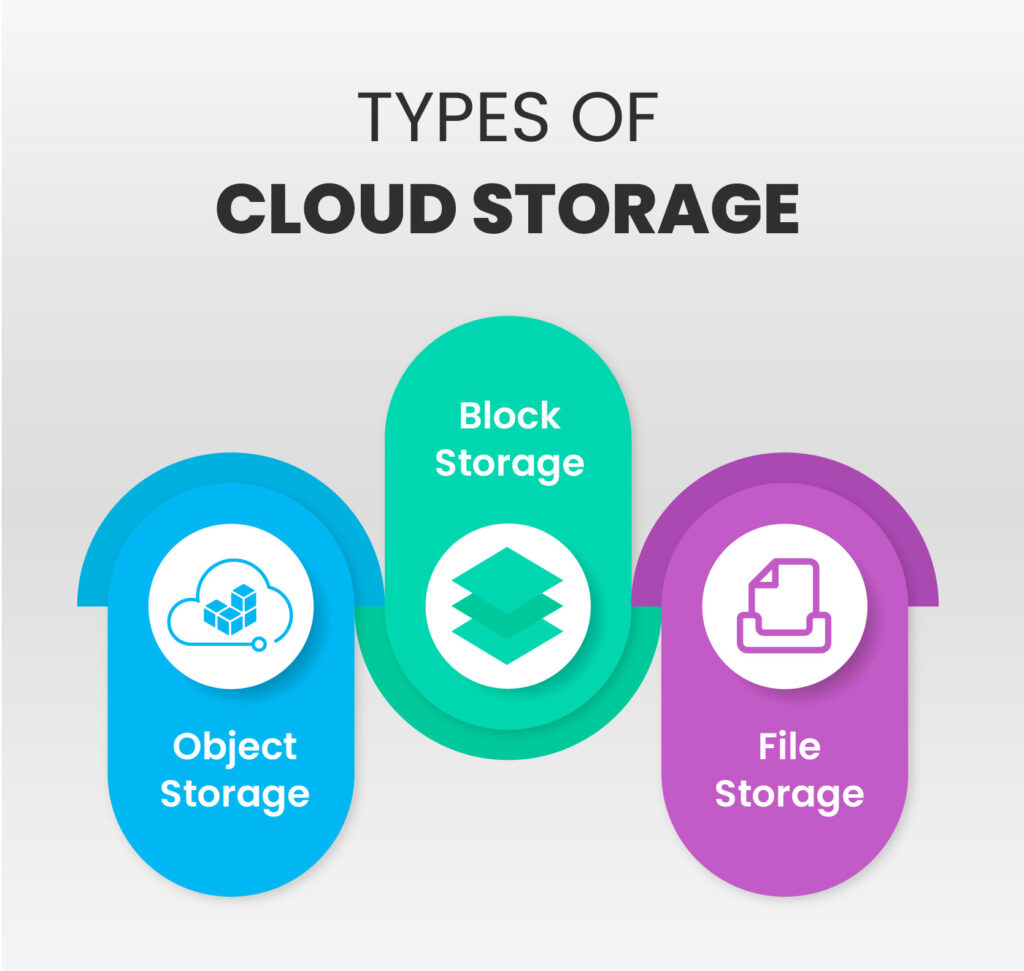
Within the sphere of cloud storage, there are several options tailored to specific needs:
Object Storage: Ideal for storing and managing large volumes of unstructured data like multimedia files or documents. Prominent object storage services include Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage.
File Storage: This service is akin to traditional file systems and is apt for organizations that need shared access to files. Notable examples include Amazon EFS and Azure Files.
Block Storage: Offering raw storage volumes that can be attached to virtual machines, block storage is often used when running databases or other applications that require direct access to storage devices. AWS EBS and Azure Disk Storage are well-known block storage services.
Benefits of Cloud Data Storage
As businesses race towards a data-driven future, cloud data storage offers a multitude of benefits that empower organizations to manage their data assets more effectively. Let’s explore some of these key advantages:
Scalability:
The scalability of cloud storage is one of its most compelling attributes. It allows organizations to efficiently adjust their storage needs in response to growth, reducing the need for significant upfront investments in physical hardware. As data requirements expand, additional storage space can be provisioned seamlessly, ensuring that businesses can keep pace with evolving data demands.
Accessibility:
Cloud storage extends accessibility to data like never before. It breaks down geographical barriers, allowing teams and collaborators across the world to work together in real-time. This enhanced accessibility enhances productivity and drives effective collaboration, as data is readily available from any location with internet connectivity.
Cost-Efficiency:
Traditionally, building and maintaining on-premises data storage infrastructure incurred substantial capital and operational costs. Cloud storage replaces these expenses with a scalable, pay-as-you-go model. With no need to invest in physical hardware or perform ongoing maintenance, cloud storage provides significant cost savings for businesses. Moreover, you only pay for the storage you consume, optimizing cost-efficiency.
With these advantages, it’s no wonder that organizations of all sizes are turning to cloud data storage to meet their data management and storage needs. Yet, navigating the vast landscape of cloud data storage solutions can be complex. One of the first decisions businesses must make is selecting the right cloud storage provider.
Selecting the Right Cloud Storage Provider
Choosing the right cloud storage provider is a pivotal decision. A careful selection ensures that your organization’s data assets are secure, accessible, and well-managed. Here are some essential considerations when evaluating cloud storage providers:
- Critical Evaluation: When choosing a cloud storage provider, it’s crucial to evaluate multiple factors:
Data Security: Assess the provider’s security protocols, encryption standards, and compliance certifications to ensure your data remains protected.
Service-Level Agreements (SLAs): Understand the SLAs in place, which define the provider’s commitment to service uptime, support responsiveness, and data availability.
Pricing Structures: Grasp the pricing model to avoid unexpected costs. Many providers offer free tiers with limitations or pay-as-you-go plans based on usage. - Leading Cloud Storage Providers: The cloud storage landscape is populated with several major players who offer reliable and scalable storage solutions:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is renowned for its vast selection of storage services, such as Amazon S3 for object storage and EBS for block storage.
Microsoft Azure: Azure provides versatile storage solutions, including Azure Blob Storage and Azure Files for various use cases. Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP delivers robust cloud storage options, like Google Cloud Storage and Cloud Filestore.
Evaluating each provider’s features and strengths will guide you toward selecting the one that aligns best with your organization’s specific requirements. Remember, the right choice can significantly impact your data management, accessibility, and overall operational efficiency.
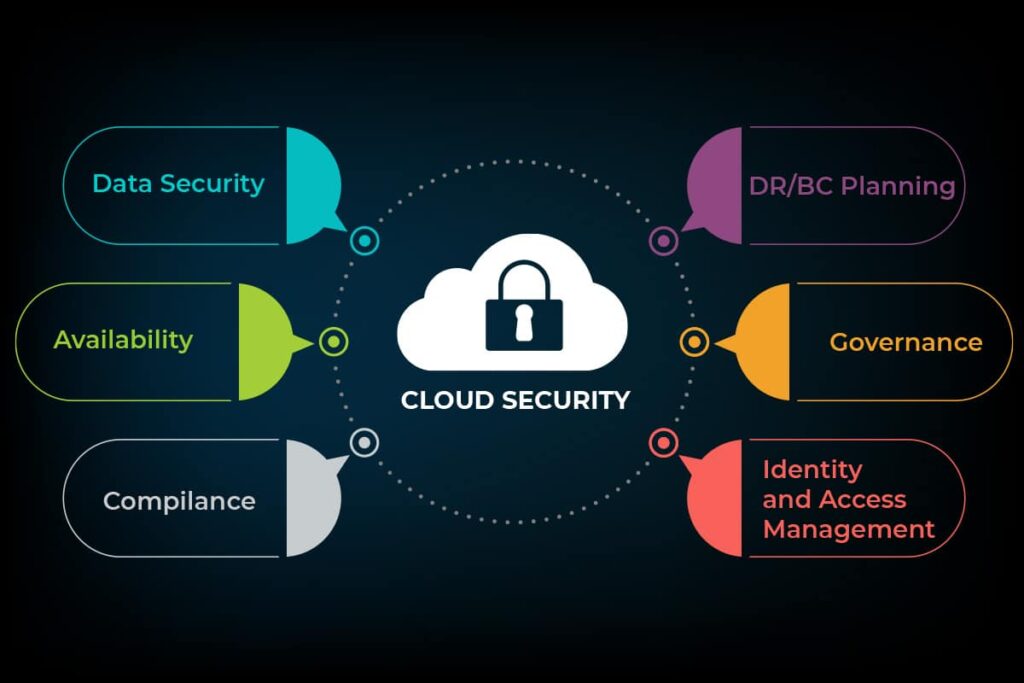
Data Security in the Cloud
While the benefits of cloud data storage are undeniable, data security remains a paramount concern. When data is stored in the cloud, businesses must rely on their chosen provider to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data. However, the shared responsibility model dictates that users also have a crucial role in securing their data.
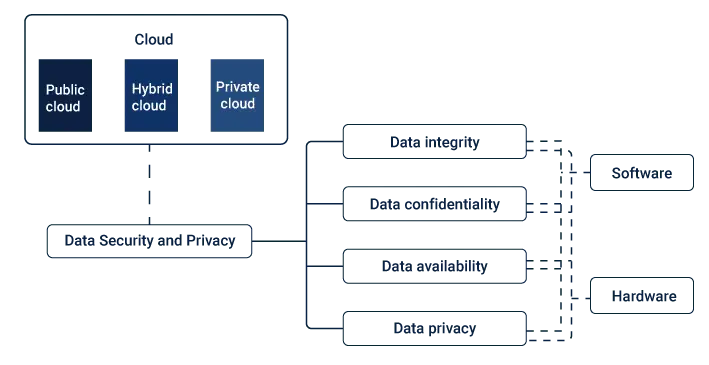
Data Security Responsibility
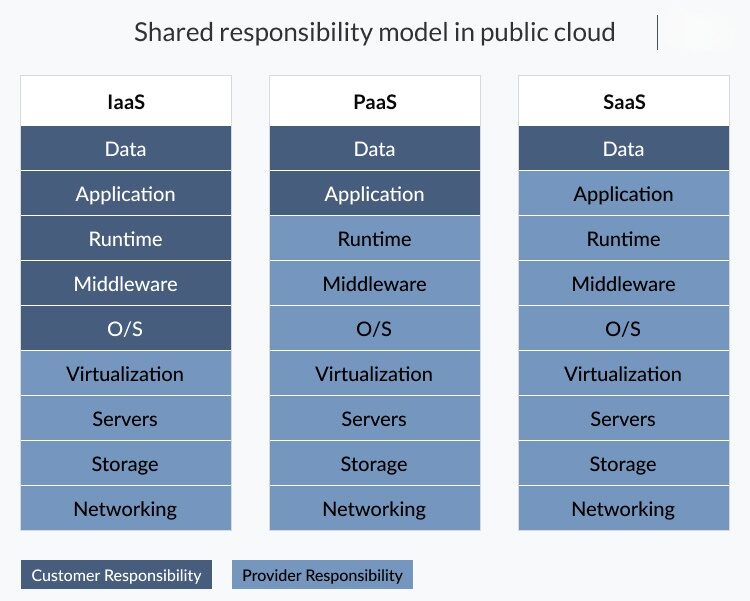
Shared Responsibility Model:
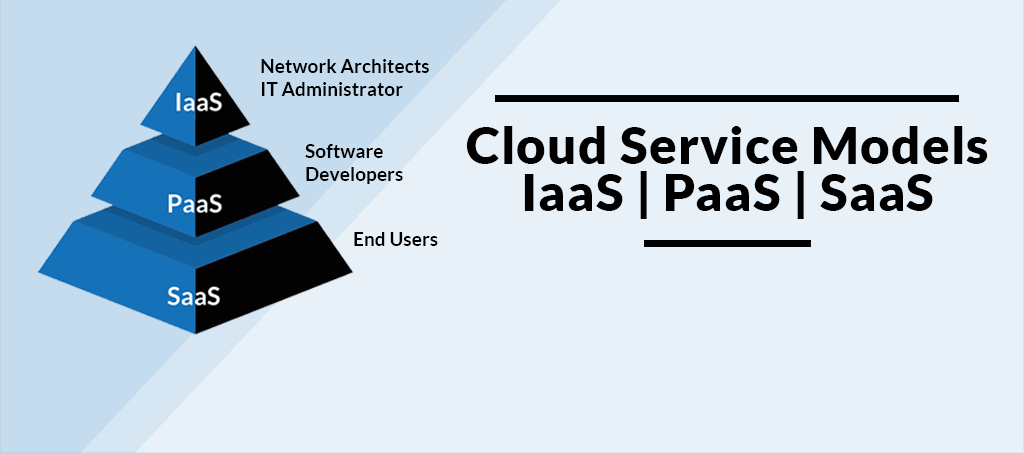
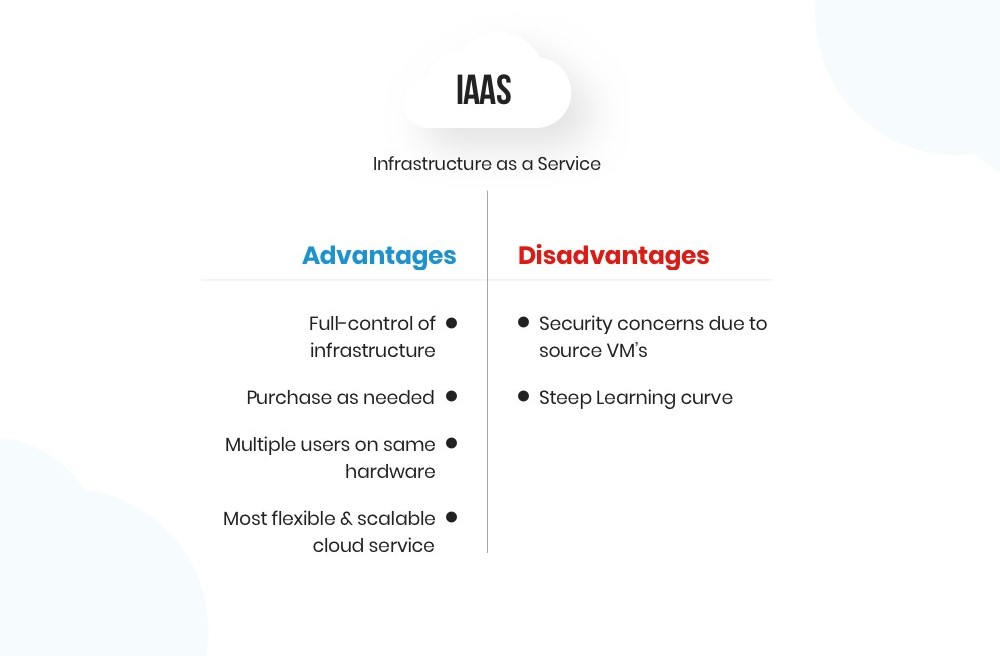
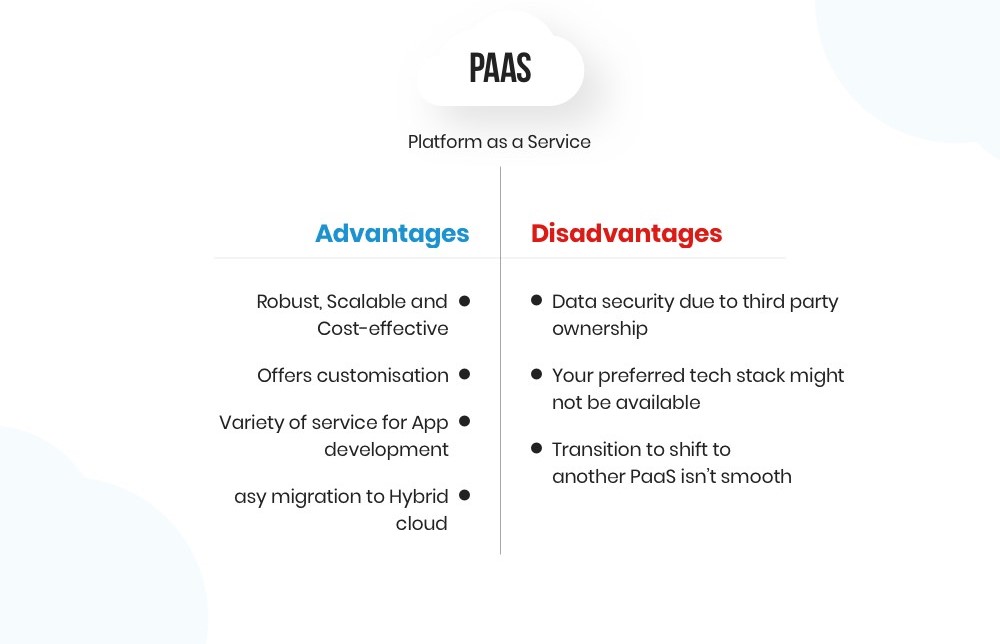
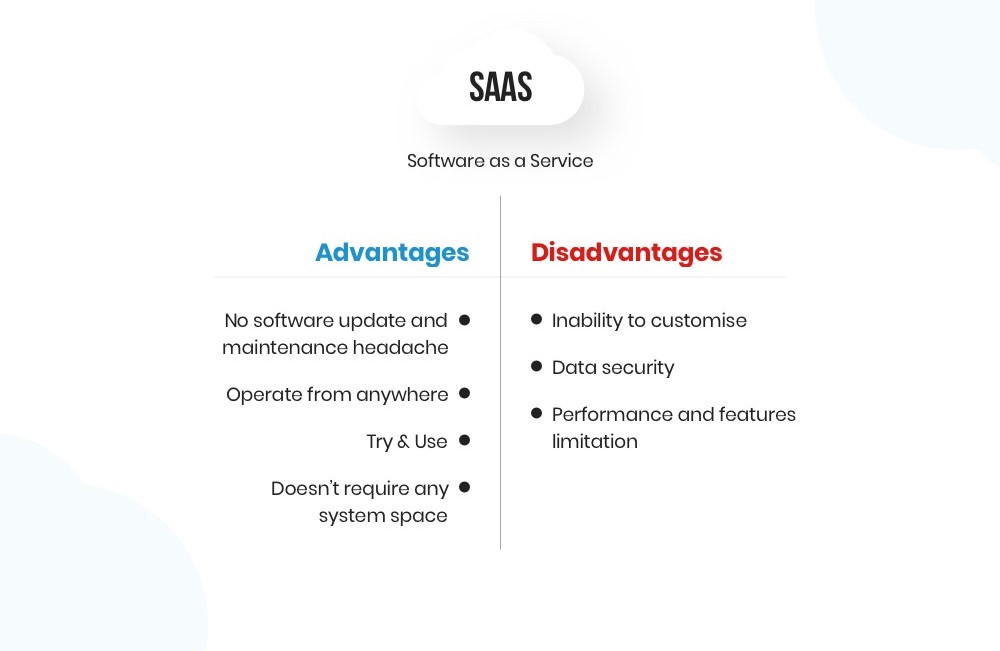
One of the fundamental principles of cloud data security is the shared responsibility model. It distinguishes between the responsibilities of the cloud service provider (CSP) and the user, and it varies depending on the cloud service model—Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS). It’s essential to understand where your responsibilities lie and implement appropriate security measures.
Users’ Role in Data Security:
In this shared responsibility model, users must shoulder the responsibility for safeguarding their data and applications. In this regard, it’s important to understand that while cloud providers manage the security of their infrastructure, users hold a critical role in securing the data and applications they store in the cloud.
Importance of Data Encryption:
Data encryption is a fundamental aspect of cloud data security. It ensures that even if data is intercepted or compromised, it remains indecipherable. Utilizing encryption for data at rest and data in transit adds an extra layer of security.
Best Practices for Optimizing Cloud Data Storage
As organizations delve deeper into the cloud data storage landscape, adopting best practices is paramount for maintaining data security, optimizing storage, and realizing the full potential of cloud storage solutions. Here are some essential best practices:
Regular Data Backups:
Schedule regular backups to ensure data recovery in case of unexpected data loss or system failures. Cloud storage solutions often provide automated backup options for added convenience.
Data Classification and Access Control:
Classify your data into categories based on sensitivity and implement access controls to restrict data access to authorized users. This practice minimizes the risk of data breaches.
Data Lifecycle Management:
Implement a comprehensive data lifecycle strategy that includes data retention, archiving, and secure disposal. Proper data lifecycle management optimizes storage usage and ensures compliance with data regulations.
Data Redundancy and High Availability:
Leverage data redundancy to ensure high availability. By replicating data across multiple servers or geographic locations, you can maintain data accessibility even in the event of hardware failures or regional outages.
Monitoring and Auditing:
Employ robust monitoring and auditing tools to keep a watchful eye on your data storage. These tools provide real-time insights into data access, anomalies, and potential security threats.
With these best practices in place, your organization can harness the power of cloud data storage while safeguarding your critical data assets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cloud data storage solutions have redefined the way businesses manage their data, offering scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency. However, selecting the right cloud storage provider and adhering to data security best practices are pivotal for a successful cloud data storage strategy. As organizations continue to embrace the digital age, cloud data storage remains a fundamental component in achieving data-driven success.
By understanding the nuances of cloud data storage, embracing data security responsibilities, and implementing best practices, organizations can embark on a journey that optimizes data management, drives collaboration, and fuels their growth in the data-driven future. So, when it comes to data storage, remember that the cloud is not just a place to store data; it’s a platform to unlock the potential of your data.
Follow this page to know more about 7 Benefits of 24/7 Managed IT Support .