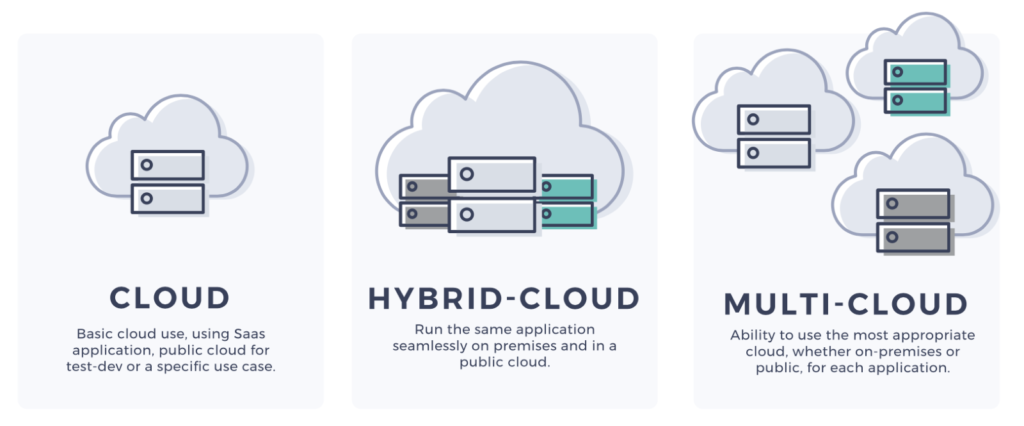
The world of cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate. Among the newest trends is the adoption Pros and Cons of multi-cloud strategies. This approach involves utilizing services from multiple cloud providers to meet various business needs. While multi-cloud offers substantial benefits, it comes with its set of challenges. In this post, we’ll explore the ins and outs of multi-cloud strategies to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the advantages and disadvantages.
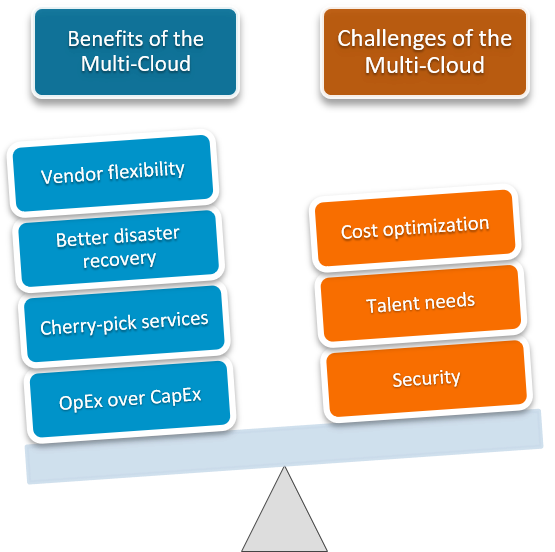
Pros of Multi-Cloud Strategies:
- Reduced Vendor Lock-In: Multi-cloud provides businesses with the freedom to avoid total dependence on a single cloud provider. This flexibility enables organizations to switch to other providers when necessary, reducing the risk of getting locked into a single vendor.
- Enhanced Performance: Multi-cloud allows companies to select the best cloud provider for specific workloads. This tailored approach can lead to significant improvements in performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Disaster Recovery and Redundancy: By dispersing data and applications across multiple cloud platforms, companies can significantly bolster their disaster recovery capabilities. This minimizes downtime and data loss, which is essential for business continuity.
- Compliance and Data Residency: Multi-cloud architectures can be fine-tuned to adhere to regional data residency regulations by storing data in geographically suitable data centers. This is especially important for global companies grappling with diverse regulatory requirements.
- Cost Optimization: The allure of multi-cloud lies in its potential for cost-effectiveness. Companies can choose cost-efficient services from various providers, ensuring that cloud expenses remain manageable.
Cons of Multi-Cloud Strategies:
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud environments can be a complex task. It requires a robust strategy for deployment, monitoring, and governance. This complexity can lead to operational challenges and potential security risks.
- Increased Costs: Although cost optimization is appealing, keeping cloud costs in check is essential. Without rigorous resource management, the expenses of managing multiple providers might surpass the benefits.
- Interoperability and Integration: Seamless integration of services and data across different cloud platforms can be challenging. Achieving smooth interoperability and data transfer between providers requires meticulous planning and execution.
- Security and Compliance: Safeguarding data and applications in a multi-cloud environment can be more demanding due to the varying security models, policies, and compliance standards across providers. Robust security measures and compliance practices are crucial.
- Skills and Expertise: Maintaining a multi-cloud infrastructure requires skilled professionals who understand the nuances of each cloud provider. Finding, training, and retaining these experts can be a significant challenge.
Conclusion
In summary, Pros and Cons of multi-cloud strategies offer numerous advantages, including reduced vendor lock-in, improved performance, and increased redundancy. However, they also come with challenges related to complexity, cost management, security, and integration. The decision to adopt a multi-cloud approach should align with a company’s specific requirements, objectives, and resource availability. Thorough planning and diligent management are essential for a successful multi-cloud implementation. By navigating the cloud landscape thoughtfully, organizations can leverage the full potential of multi-cloud strategies while mitigating potential obstacles, thus unlocking the key to more resilient, flexible, and cost-effective cloud operations.



