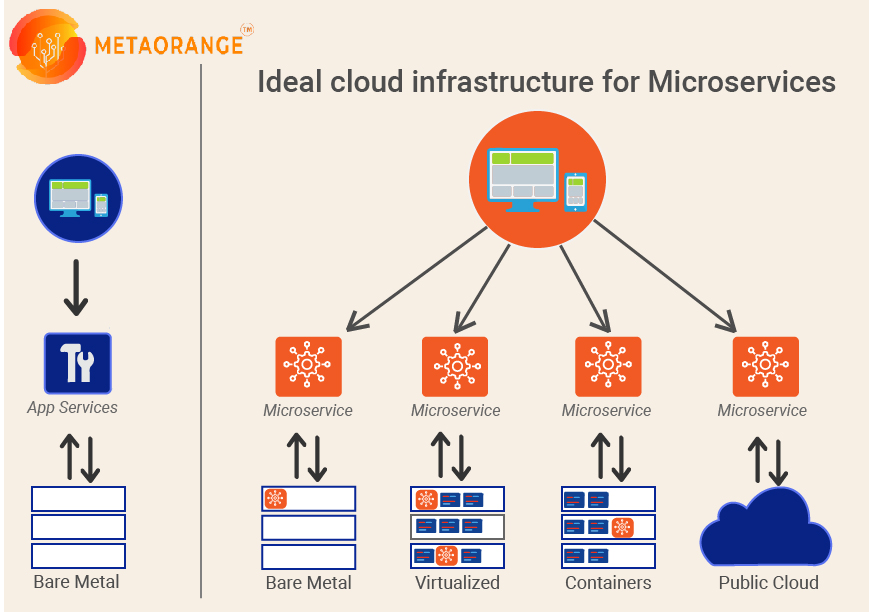
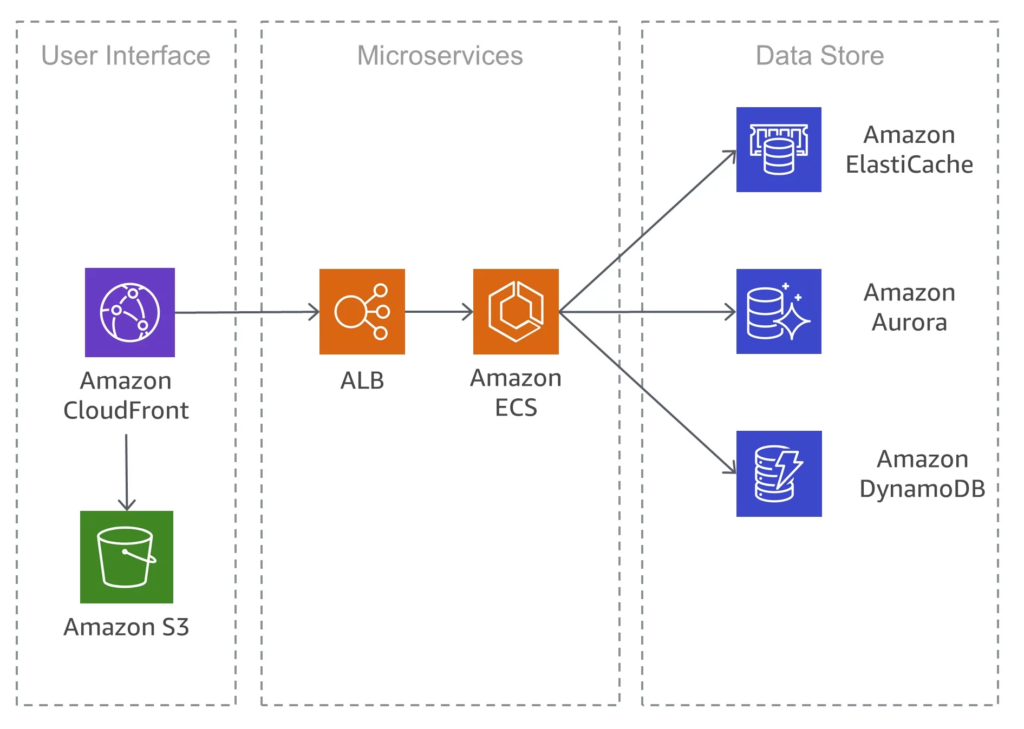
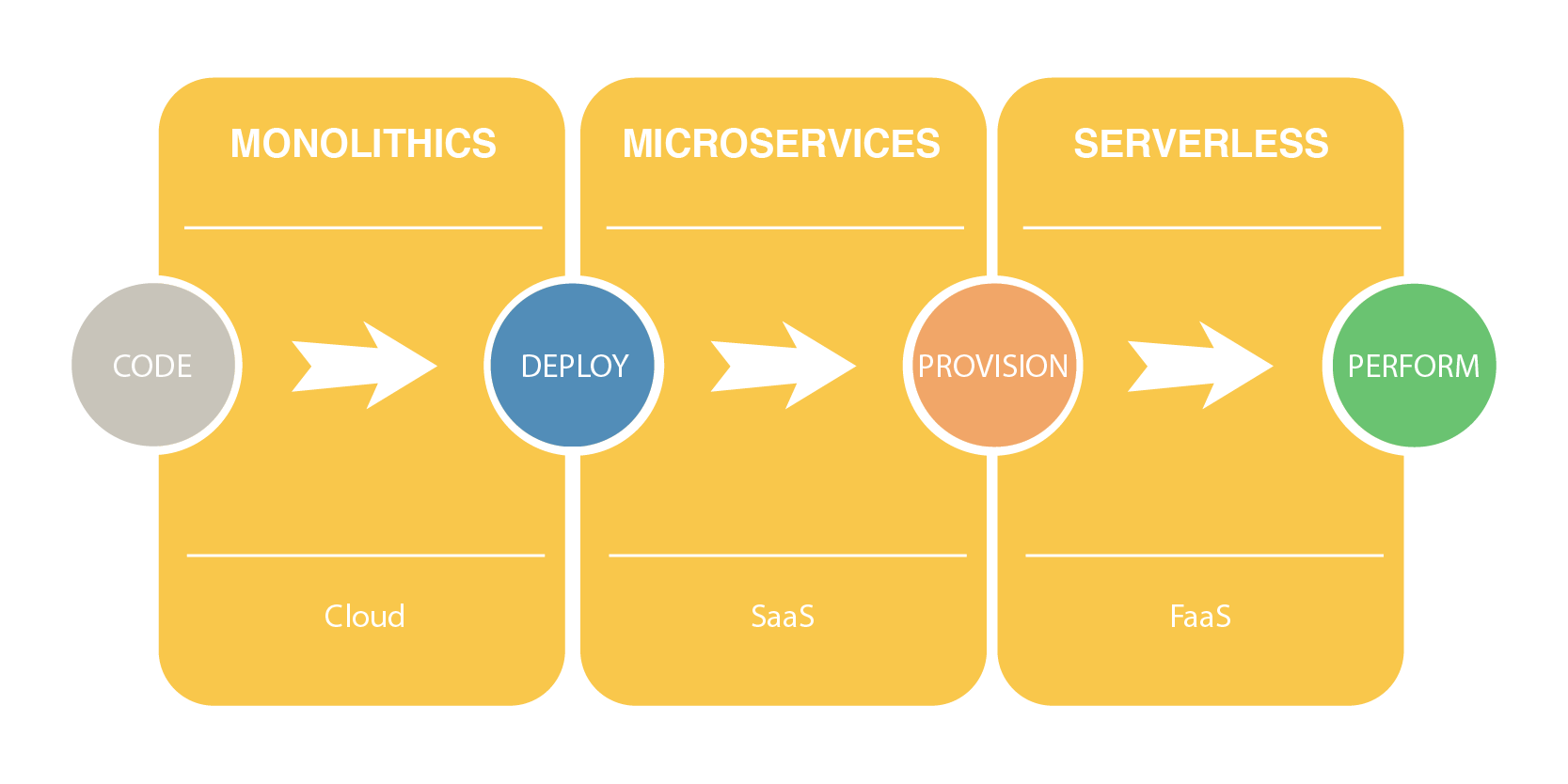
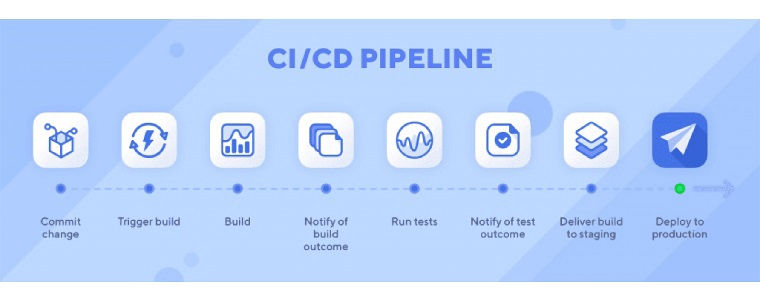
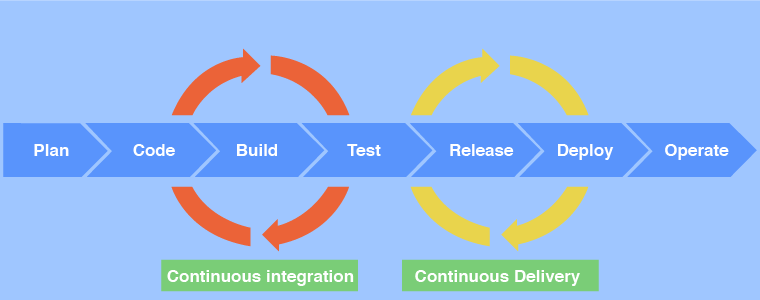
If you are using a Low-code or No-code platform, you may have faced difficulty accessing data from legacy systems like old databases and software modules. Such a challenge can stall your entire progress.
We at Metaorange Digital have brought you a few approaches to help integrate your low-code and no-code platforms with legacy systems.
Introduction to Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Low Code and No Code systems are software development platforms that use libraries to create systems without the need for coding or minimal coding. These libraries are popular, but a growing challenge for them is to integrate with legacy systems that cannot be modernized for several reasons.
The popularity of low-code/no-code platforms is on the rise, driven by their numerous advantages. With the current market estimated to be worth $22.5 billion and growing worldwide, this trend shows no sign of slowing down. Some of the key growth drivers include freelancers, small-scale developers, small business owners, citizen developers, and students.
Popular applications like WordPress, Zapier, Airtable, Webflow, etc., enable even non-technical staff, entrepreneurs, and business professionals to create stunning websites, software, and other systems. Low-code and No-code platforms also help companies develop faster software, resulting in fewer errors.
The global market for low code(and no code) market is currently valued at $22.5 Billion as of late 2022. By 2024, the market is estimated to grow to the size of $32 Billion. Therefore, the need to address the incompatibility between these and the old systems becomes paramount.
Building from scratch vs. modernizing with Low-Code and No-Code solutions
Building new systems and integrating with legacy systems are valid approaches, but sometimes, when legacy systems are gigantic, building new systems becomes costly. Even for a small system, the cost may reach up to $70,000. However, old systems only get eliminated after a considerable time. Integrating low-code and no-code platforms with legacy systems is, therefore, a ubiquitous challenge. To help you, we have compiled a few approaches that can solve your codeless development journey.
Integrating Low-Code and No-Code
Here are a few tried and tested strategies to help you integrate these systems with any legacy system you need.
Application-Program Interface
APIs are one of the most common ways to integrate low-code/no-code platforms with legacy systems. These are the software intermediaries that help two systems exchange information with each other. This allows the low code/no code platform to communicate with the legacy system and exchange data.
A few common examples of APIs are Twitter bots and Crypto.com widgets for WordPress.
Data integration
You can use data integration tools to extract data from the legacy system and import it into the low code/no code platform. This allows the low code/no code platform to access and use the legacy data.
Middleware
Middleware is software that acts as a connection between two systems. They relay information both ways and help ensure proper functioning. Middleware can bridge the low code/no code platform and the legacy system. It can handle the data and API communication between the two systems and translate between different data formats.
Custom Code:
In some cases, custom code may need to be written to integrate the low code/no code platform with the legacy system. This application may be necessary if the legacy system does not have APIs or the data formats are incompatible.
Custom CSS that is being used in WordPress is a typical example
Please Note
It’s essential to carefully consider the approach that will work best for a particular organization based on the specific legacy systems and data involved, as well as the goals and constraints of the integration project.
An experienced development team and thorough testing can help ensure a successful integration. Metaorange Digital can help you integrate legacy systems with your no-code or low-code platform. This method can help you develop with expert assistance.
Book a 15-minute discovery call to know more
3 Essential Points to be Taken Care of
These next-generation systems have several benefits, such as low development time and greater collaboration. However, there are also a few points to consider when integrating low-code or no-code platforms with legacy systems. Addressing these topics ensure that your systems do not encounter any significant problems in the future.
Security
Security should be a top priority when integrating low-code/no-code platforms with legacy systems. Ensure that proper security measures, such as encryption and authentication, are in place to protect sensitive data. T-Mobile was hacked, and hackers stole 37 Million account data in an API breach.
User experience
It’s essential to ensure that the user experience is consistent and seamless across the Low-code and No-code platforms and the legacy system. This factor can help reduce confusion and improve adoption among users.
Maintenance
Integrating the low code/no code platform and the legacy system will require ongoing maintenance and support. This may include updating APIs or data integration tools, fixing bugs, or handling compatibility issues. Plan for adequate resources and budget to ensure the integration is maintained and runs smoothly over time.
Metaorange Digital can help you ensure smooth integration with legacy systems and also ensure that your developed systems perform as expected.
Conclusion
Legacy systems were not meant to work with no code platforms. However, with technological developments and the rising need for accurate, fast, and low-cost development, no-code and low-code systems have gained popularity. However, they need to communicate with legacy systems more readily. For bridging these systems, there are several approaches, such as APIs, Middleware, and Custom Coding.
These approaches can solve your issues, but maintaining and securing them are further challenges. Metaorange Digital helps you tackle these challenges with ease and enables you to develop no-code and low-code solutions swiftly, securely, and reliably.
Learn More – Cloud Transformation Services of MetaOrange Digital